Texture
See highlights and high-quality resources for advanced investigations.
Texture (an element of visual art and design) is the
perceived surface quality of a work of art...
characterized by its visual and physical properties...
—

Texture at
oogle Arts & Culture
Intro Video: Texture: 7 Elements of Art (7:24) —Lillian Gray
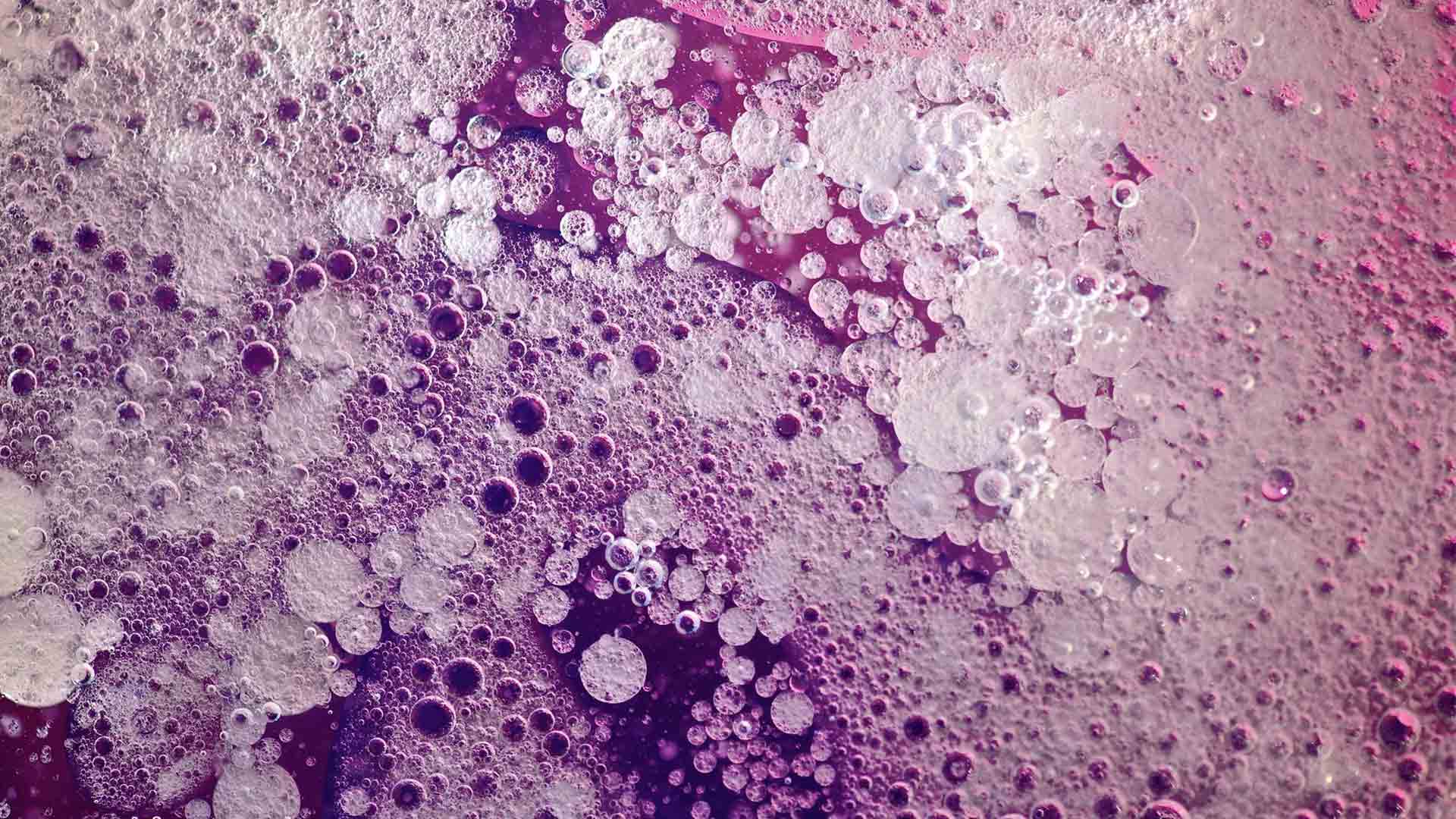
Physical Texture:
Physical, actual, tactile texture
is the patterns of variations upon a solid surface.
These can include -- but are not limited to -
fur, canvas, wood grain, sand, leather, satin, eggshell, matte,
or smooth surfaces such as metal or glass...
—
Next, we will learn about "implied, visual" textures and common techniques to draw the illusion of "realistic" textures.
Visual Texture
Visual or implied texture is the illusion of having physical texture...
—
Hatching Crosshatching Stippling Blending
are four of the most common line techniques used to create value and the "illusion" of space and texture on a form in a drawing and they can be applied with all drawing mediums. We begin with Hatching by Philinthecircle.